hepatitis
hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections, but can also result from toxins (including alcohol and certain medications), autoimmune conditions, and other infections. the most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis a, b, and c.
hepatitis a is usually spread through contaminated food or water and generally leads to a self-limited disease. hepatitis b and c are typically transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids and can lead to chronic disease, leading to long-term liver damage and increasing the risk of liver cancer.
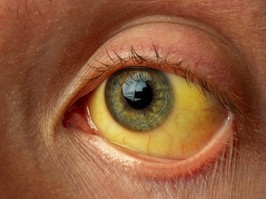
symptoms of hepatitis can include fatigue, nausea, poor appetite, belly pain, a mild fever, or yellow skin or eyes (jaundice). some types of hepatitis may cause no symptoms and can silently progress and damage the liver.
diagnosis of hepatitis involves blood tests, which can detect signs of inflammation and the presence of viral infections. imaging tests and liver biopsies may be used for a more detailed assessment.
treatment depends on the type and stage of hepatitis. hepatitis a often doesn't require treatment other than rest and hydration. chronic hepatitis b and c may be treated with antiviral medications. lifestyle changes, including avoiding alcohol and managing other health conditions, are also important.
preventive measures include vaccines for hepatitis a and b, practicing safe sex, using sterile needles, and avoiding sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes.