crohn's disease
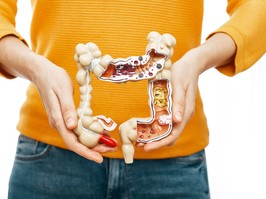
crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (ibd) that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus, although it most commonly affects the end of the small intestine and the beginning of the colon. crohn's disease is characterized by inflammation that spreads deep into the layers of affected bowel tissue.
symptoms of crohn's disease can range from mild to severe and often develop gradually. they include diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, blood in the stool, ulcers, reduced appetite and weight loss, and fever.
the exact cause of crohn's disease is unknown, but it's believed to result from a complex interaction of genetic, environmental, and immune factors.
diagnosis involves a range of tests, including blood tests, stool tests, colonoscopy, endoscopy, and imaging studies like ct scans or mri.
treatment aims to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, and prevent flare-ups, using medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, and antibiotics. in severe cases, surgery to remove a damaged portion of the digestive tract may be necessary.
lifestyle and dietary changes can help manage symptoms and maintain remission.