stroke
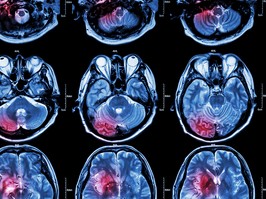
a stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. brain cells begin to die in minutes. a stroke is a medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial to minimize brain damage and potential complications.
there are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. symptoms of a stroke can include trouble speaking and understanding what others are saying, paralysis or numbness of the face, arm, or leg, problems seeing in one or both eyes, headache, and trouble walking.
risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure, tobacco use, heart disease, diabetes, and certain blood disorders.
treatment depends on the type of stroke. ischemic strokes are treated with blood clot-busting drugs, and hemorrhagic strokes are treated by controlling the bleeding and reducing the pressure in the brain.
recovery and rehabilitation are an important part of stroke treatment, helping individuals regain lost skills and adjust to any residual disabilities.