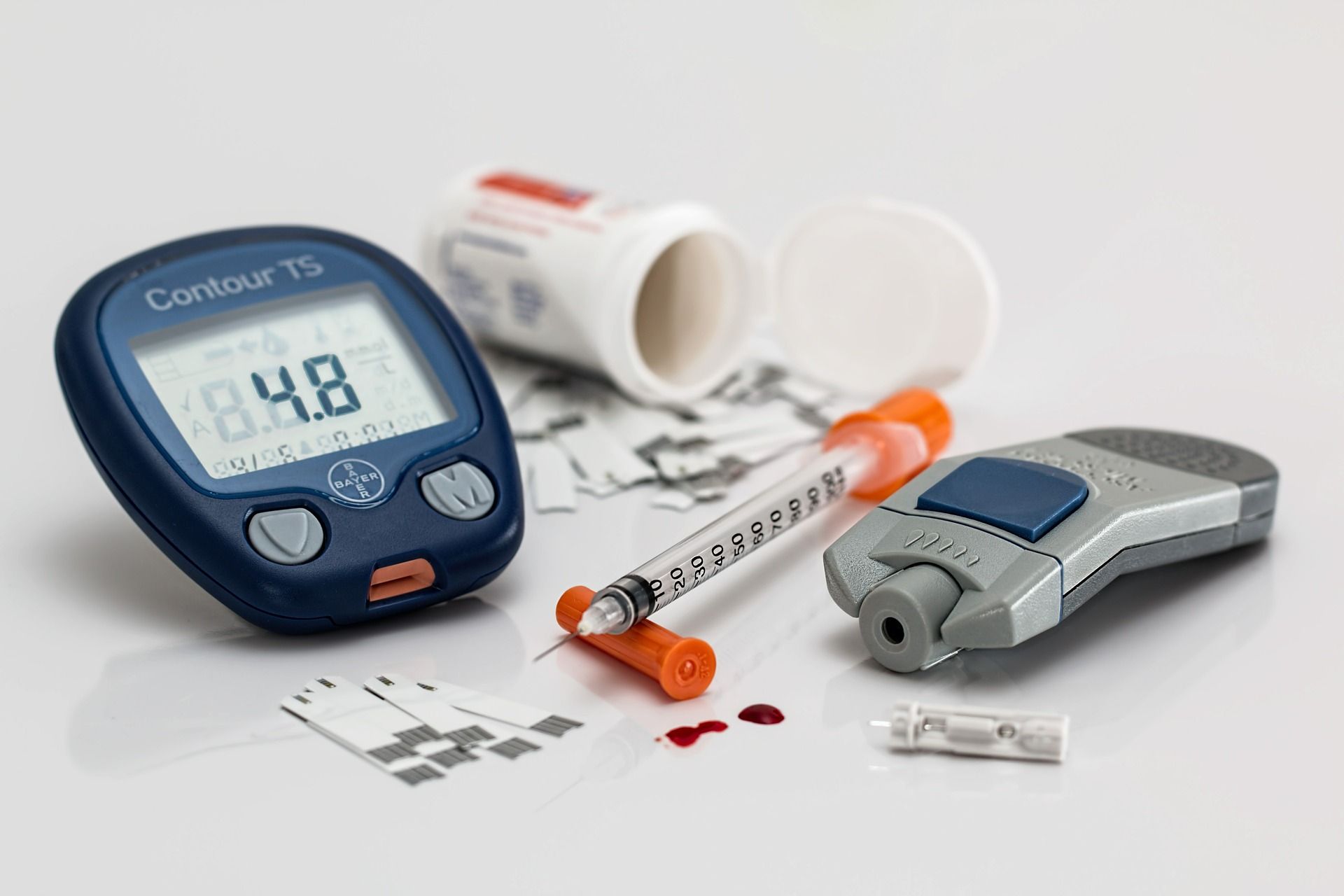
degludec is taken once a day and begins to work a few hours after injection. it can remain effective longer than 24 hours.
“when we first discovered insulin, it was the shorter-acting insulin,” says jain. “but what happens is that it’ll have a peak and then it’ll clear out from the body. so that necessitated having multiple injections. but that’s not how the pancreas works in the body. our brain requires sugar on an ongoing basis and when we are not eating, obviously the brain still requires sugar.”
he explains that the liver is the warehouse for storage of sugar, breaking down sugar stores and releasing them into the blood supply. “but with diabetes, unfortunately the liver is leaking far more glucose, so you need some insulin in the background to prevent the liver from leaking too much glucose into the bloodstream. so this is where having a long-acting insulin makes a big difference, because the long-acting insulin is what will counteract the excess leakage of sugar from the liver.”
continuous glucose monitoring
instead of the need for frequent finger pricks to determine blood sugar levels, a continuous glucose monitor (cgm) is a wearable sensor and transmitter that tracks blood sugar throughout the day and night. the readings are relayed in real-time to a device and app for the patient, caregiver or healthcare provider, and can be a lifesaver for people who experience low glucose during the night. some cgm, brands like dexcom g7 and medtronic guardian connect system, can also be paired with an insulin pump.
 8 minute read
8 minute read